Top 11 Types of Healthcare Software to Know in 2026

The healthcare market has been in boom from the last few years and it is recently estimated that the Global healthcare IT market is estimated to reach $660 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 15.8%.
Against the backdrop of the coronavirus pandemic, which has catalyzed the adoption of innovative technologies and software solutions, the rapid digital transformation of the healthcare industry is in full bloom. The healthcare software market was still in its infancy, and many healthcare providers were using outdated systems and manual processes before the pandemic.
Flash forward to the present, and health care has changed dramatically and at breakneck velocity, and software solutions are now integral to everything from patient care to administrative efficiency. National governments around the world are demanding modernization, advocating for more private, technology-aided approaches to healthcare app development that will ensure better outcomes, greater access, and streamlined operations.
Now, one software solution alone cannot meet all the diverse needs of the healthcare industry. Here are some of the types of healthcare software that providers are embracing to interact and create a streamlined, effective environment when they are utilized together. But first, let’s get to the meaning.
What is Healthcare Software?
Healthcare software, in its simplest form, comprises digital tools and systems that healthcare providers use to manage, streamline, and improve aspects of healthcare services. Software solutions are extremely helpful in enhancing the quality of care, increasing operational efficiency, and ensuring better patient outcomes.
Healthcare software has much in common with consumer health apps, such as fitness trackers or sleep monitors, so much so that there’s a fine line between the two.
One type of healthcare software that affects diagnosis and treatment is electronic health records (EHR), systems that doctors use to keep track of patients’ medical histories as well as medications. A fitness tracker like Fitbit, on the other hand, enables users to track their steps or sleep patterns but does not provide medical advice or diagnosis.
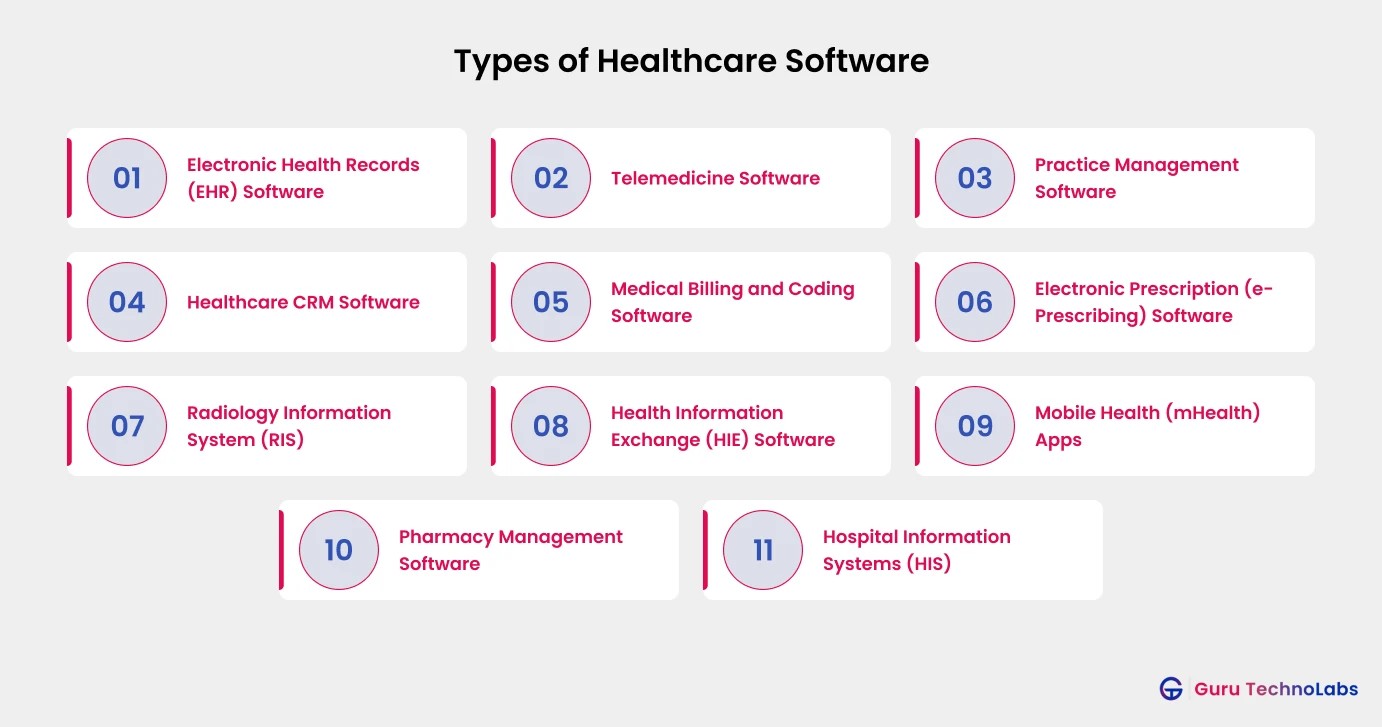
Most Popular Types of Healthcare Software
The list below is certainly selective as we have tried to jot down the most popular types of healthcare software, including features and use cases, each playing an important role in making the healthcare system advanced and efficient.
1) Electronic Health Records (EHR) Software
EHR software provides digital storage and management of patients’ medical records, designed to streamline how healthcare providers access, update, and share patient information.
EHRs, unlike traditional paper-based records, help in streamlining workflows, reduce errors, and ensure that all healthcare professionals involved in a patient’s care are well up to date with the latest information. It’s a cornerstone of modern health care, enabling health care providers to access complete and accurate patient histories.
Features
- Real-time access to patient data across healthcare settings.
- Encryption is used to keep patient privacy by securing stored data.
- Accessing health information through patient portals
- Integration across labs and radiology Lab orders and results Prescriptions.
- Decision support tools can help in formulating clinical decisions.
Use Cases
| Hospitals | Clinics | Ambulatory Settings |
|---|---|---|
| EHRs allow doctors, nurses, and specialists to access a patient’s history in real time. | Smaller healthcare providers benefit from simplified documentation, easy billing integration, and improved patient communication. | EHRs help manage patient flow and keep track of chronic conditions, improving follow-up care and reducing errors in prescriptions. |
2) Telemedicine Software
Telemedicine software lets the healthcare provider to have a conversation with patients remotely by using online communication tools like video calls and chats, or other communication forms. It is revolutionizing the healthcare industry by making medical consultations more accessible to patients located in remote locations or those with mobility problems.
This software was a strong force during the covid-19 lockdown as patients received their help from healthcare professionals without stepping out of their homes.
With the growing adoption of AI in telemedicine, healthcare providers can now enhance virtual consultations with smart diagnostics and real-time monitoring.
Features
- For rural consultations, video conferencing is used.
- Booking appointments , along with alerts and reminders.
- Text-based message thing.
- It is an online medication prescribing service provided for doctors.
- Extraction of patient data during consultations with EHR systems.
Use Cases
| Rural health care providers | Urgent care clinics | Mental health services |
|---|---|---|
| Telemedicine allows rural patients to receive care from specialists without the need to travel long distances. | Telemedicine software helps extend care beyond office hours, providing patients with quick consultations when they need it most. | Therapists and counselors use telemedicine to offer virtual therapy sessions, providing greater flexibility for patients and reducing the stigma associated with in-person visits. |
3) Practice Management Software
This is the software that allows the healthcare practice to have its operations streamlined. It helps in appointment scheduling, registration, billing, stock and staff management, and much more.
So, this software must be determined to make their life easier; therefore, the solution will have dedicated software to maximize efficiency and allow healthcare providers to spend more time treating patients than managing their administration.
Features
- Scheduling appointments with reminders.
- Insurance claims and patient payment management billing and invoicing features
- Tracking patient movement to reduce wait times and staff placement
- Tools for financial, operational, and clinical reporting.
- Staffing – Simple staff scheduling and payroll management
Use Cases
| Private Practices | Dental Clinics | Multi-physician Clinics |
|---|---|---|
| Automate daily operations, from patient scheduling to processing payments, improving efficiency and reducing errors. | A dental practice uses this software to track patient appointments, manage dental records, and handle insurance claims seamlessly. | A healthcare center with multiple specialists benefits from a unified practice management system that coordinates all aspects of patient care and administrative tasks. |
4) Healthcare CRM Software
Healthcare CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software is designed to help healthcare providers manage interactions with patients, prospects, and referring physicians. It centralizes patient data, including contact information, medical history, and communication preferences, to improve relationships and increase patient satisfaction.
This software not only helps retain existing patients but also supports marketing efforts by tracking patient behaviour and communication trends.
Features
- Patient segmentation for targeted communication and marketing campaigns.
- Appointment reminders via texts, emails, or phone calls.
- Follow-up tracking for ongoing patient care and relationship management.
- Data analytics to gain insights into patient behavior and needs.
- Lead management to track prospects and referrals.
Use Cases
| Hospitals | Specialists Practices | Health Insurance Companies |
|---|---|---|
| CRM helps hospitals manage patient communication, improving engagement and retention. | A cardiology practice uses CRM to track appointments and send follow-up reminders. | Health insurers use CRM to track interactions and streamline claims processing. |
5) Medical Billing and Coding Software
Indeed, these programs are necessary for making sure that the right healthcare services are accounted for and billed to insurance companies or patients. This software allows medical coders and billing specialists to convert patient diagnoses and treatment into standardized codes that are used to process claims.
It eliminates human errors, accelerates claim processing, and guarantees adherence to health insurance rules.
Features
- Coding automation for procedures and diagnosis.
- Claim submission direct to the insurance companies.
- Integrated payment processing for insurance and patient payments.
- Companies whose tracking means coding under current regulation.
- Financial statements analysis and auditing reports.
Use Cases
| Hospitals | Physician Practices | Insurance Providers |
|---|---|---|
| Medical billing software streamlines billing, reducing errors and improving cash flow. | Small clinics use billing software to accurately handle claims without a dedicated billing team. | Coding software helps insurance companies ensure accurate claims and minimize payment disputes. |
6) Electronic Prescription (e-Prescribing) Software
E-prescribing software enables the electronic transmission of prescriptions between healthcare providers and pharmacies, thus eliminating the use of paper prescriptions and minimizing the potential for errors. It helps in managing medication efficiently by integrating with Electronic Health Records (EHR).
It promotes adherence to rules, verifies medication safety, and improves patient comfort.
Features
- Transmit prescriptions to pharmacies instantly for efficient processing.
- Tracking medication history to avert drug interactions.
- Patient and provider automated refill requests.
- Updates about your prescription status in real time.
- Regulatory compliance with local and national laws.
Use Cases
| Hospitals |
|---|
| E-prescribing software reduces medication errors and improves patient safety by sending prescriptions directly to pharmacies. |
7) Radiology Information System (RIS)
Radiology Information Systems (RIS) are critical for managing radiology imaging data across medical institutions. This software simplifies the management of images, patient records, and radiology reports, ensuring faster access and more accurate diagnosis.
By integrating with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), RIS enables healthcare providers to streamline imaging workflows and enhance collaboration across departments.
Features
- Image storage and retrieval for easy access and sharing.
- Patient tracking across imagining processes and reports.
- Reporting capabilities for radiologists to generate diagnostic findings.
- Integration with PACS for secure, seamless image management.
- Improved data sharing for better collaboration and treatment planning.
Use Cases
| Specialized Imaging Centers | Research Institutions |
|---|---|
| Private radiology clinics use RIS to ensure smooth data management and enhance collaboration with referring physicians. | Research hospitals leverage RIS for sharing imaging data in clinical trials, facilitating faster research outcomes. |
8) Health Information Exchange (HIE) Software
In an attempt to mitigate these challenges, healthcare organizations are increasing their investment in such Health information exchange software. HIE is crucial to improving the coordination of care, decreasing redundancies, and guaranteeing that patients receive the best care regardless of where they seek treatment by providing secure, real-time access to patient data.
This is a necessity for creating a more interconnected, collaborative healthcare system.
Features
- It provides a secure data exchange that can be used by various healthcare providers.
- Therapy begets new rehabilitation technologies and guidelines.
- HIPAA-compliant security features to safeguard patient information.
- Integrate easier with EHR, lab results, and imaging data.
- Ability to interconnect across networks to integrate multiple healthcare systems.
Use Cases
| Regional Health Networks | Integrated Care Systems | Emergency Care |
|---|---|---|
| Health systems in regions like California use HIE to share patient data between hospitals, reducing redundant tests and improving care. | Integrated care facilities use HIE to provide seamless care transitions between primary care physicians and specialists. | Emergency departments use HIE to quickly access patients’ medical histories, ensuring faster and more accurate treatment. |
9) Mobile Health (mHealth) Apps
Mobile Health (mHealth) applications elevated healthcare by allowing patients to track their health right from their smartphone. Apps that monitor everything from steps to heart rates to sleep patterns enable users to take an active role in managing their health.
From mobile-based wearable devices to standalone applications, the mHealth segment is enabling end-users to remain fit and communicate with their respective doctors efficiently.
Features
- Tracking various health data such as steps, heart rate, and sleep.
- Integration with wearable devices like Fitbit and Apple Watch.
- User behavior based personalized health insights.
- Medication and appointment reminders to help adherence.
- Real-time alerts and nudges to promote healthier behaviors.
Use Cases
| Fitness Tracking | Chronic Disease Management |
|---|---|
| Brands like Fitbit and Apple Health allow users to monitor exercise routines, sleep patterns, and overall fitness, helping them make healthier lifestyle choices. | Diabetes patients use mHealth apps to track blood sugar levels and receive reminders to take medication, facilitating remote monitoring by healthcare providers. |
10) Pharmacy Management Software
Pharmacy management software has become an indispensable tool for pharmacies aiming to streamline their operations and improve patient care. From managing prescriptions to inventory control, this software ensures that pharmacies run efficiently while staying compliant with regulations.
Automating key tasks reduces the chances of errors and enhances overall operational efficiency, ultimately improving the patient experience.
Features
- Prescription management for tracking and processing patient prescriptions.
- Inventory management to ensure stock levels are optimized and medications are always available.
- Drug interaction checking to alert pharmacists of potential risks.
- Regulatory compliance with federal and local regulations (e.g., HIPPA, FDA).
- Automated billing and insurance claim submissions for faster payment processing.
Use Cases
| Community Pharmacies | Hospital Pharmacies | Online Pharmacies |
|---|---|---|
| Local pharmacies use this software to manage prescription orders, track inventory, and process insurance claims, all while improving customer satisfaction. | In large hospital settings, pharmacy management software helps track medication use across departments, improving patient safety and reducing medication errors. | eCommerce-based pharmacies leverage the software to manage inventory, track orders, and ensure timely prescription delivery to patients. |
11) Hospital Information Systems (HIS)
Hospital Information Systems are comprehensive solutions designed to manage and streamline all aspects of hospital operations, from patient care to administrative tasks.
With HIS, hospitals can effectively track patient data, monitor billing processes, manage appointments, and even support clinical decision-making. This centralized system enhances collaboration between departments and improves overall hospital management.
Features
- Patient record management with complete medical histories, lab results, and treatment plans.
- Billing and financial management for processing payments, insurance claims, and financial reports.
- Scheduling tools for appointment and operation room management.
- Clinical decision support to assist healthcare providers with accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Integration with EHR and PACS to centralize patient data and imaging information.
Use Cases
| Large Hospitals | Speciality Clinics |
|---|---|
| HIS helps large hospitals manage hundreds of daily patient admissions, appointments, and medical records, all from a single platform, improving workflow efficiency. | A cardiology clinic uses HIS to track patient visits, manage test results, and ensure timely follow-ups for patients with chronic heart conditions. |
If you want to build a custom healthcare solution like this software example, exploring custom software pricing helps you to get a clearer picture of the investment involved.
Grow Your Medical Business with Guru TechnoLabs’s Custom Healthcare Software Development
As healthcare continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, technology and digital transformation have played a vital role in reshaping the industry from its very roots. With the growing need for efficiency, accuracy, and better patient outcomes, choosing the right software can make all the difference in how healthcare providers deliver services.
If you’re planning to enter the healthcare industry, now is the perfect time to embrace this digital revolution. At Guru TechnoLabs, we specialize in custom healthcare software development and can help you tailor the perfect solution to meet your needs. Hire a dedicated team of developers from us, and you’ll not only get cutting-edge solutions but also a long-term technology partner committed to your success in this rapidly evolving field.
Looking for healthcare software that brings value to the table?
We develop compliant healthcare software for your business’s
unique requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
That is where healthcare software comes in — current healthcare software solutions automate administrative tasks, minimize errors, offer real-time data, and improve patient care and operational efficiency.
Yes, the best healthcare software today can easily integrate with existing systems (EHR, lab results supplier, pharmacy management), ensuring seamless workflows across departments and easier data accessibility.
IoT (Internet of Things) and immersive devices provide healthcare practitioners with the ability to check health metrics, allowing devices to remotely send patient data enabling better patients management and taking care of chronic diseases.
Medical software used in clinical environments is carefully regulated before being used to diagnose and treat patients, while consumer health apps are focused on allowing the user to track their wellness and not on offering warm-and-fuzzies or diagnosis advice.
These challenges include ensuring data security, integrating with existing systems, and training staff to effectively use the software — all while adhering to healthcare regulations and safeguarding patient confidentiality.