SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS: What’s the Difference and Which One Do You Need?

Cloud computing has transformed businesses’ operations, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness like never before. As the demand for digital solutions continues to rise, three cloud service models have emerged as the foundation of this evolution:
- SaaS (Software-as-a-service)
- PaaS (Platform-as-a-service) and,
- IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service)
While these terms are often used interchangeably, each serves a distinct purpose and caters to different needs within the tech ecosystem.
However, many still confuse the three, assuming they’re variations of the same concept. In reality, they offer unique levels of control, customization, and technical responsibility. Whether you’re a startup owner, developer, or IT decision-maker, understanding these differences is key to choosing the right model for your business.
Read out to explore how SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS differ, their pros and cons, and which one might be the best fit for your needs.
What does “as a service” Mean?
“As a service” means you don’t own a product or software instead, you pay to use it when you need it, usually through a subscription or pay-per-use model. The company providing the service takes care of everything, like maintenance, updates, and support, so you just focus on using what you need.
Imagine you need to use a word processor like Microsoft Word. In the past, you would buy a CD, install the software on your computer, and handle updates yourself. With “Software as a Service” (SaaS), you simply sign up for Microsoft 365 online, pay monthly fees, and use Word through your web browser.
You don’t have to install anything, worry about updates, or fix problems, the provider handles all of that. You just log in and start working.
This model is also used for other things, like streaming movies (Netflix), using business tools (Salesforce), or even accessing hardware and equipment without buying it outright.
What is SaaS (Software as a Service)?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a way of delivering software applications over the internet, where users access the software through a web browser or app without needing to install or maintain it on their devices. Instead of buying the software outright, users pay a subscription fee to use it, and the service provider handles all updates, security, and infrastructure.
Use Cases

Source: Elector IQ
SaaS is widely used across different industries and business functions due to its flexibility and ease of access. Common use cases include:
- Email and Communication: Businesses use SaaS platforms like Gmail or Outlook 365 for company-wide email and collaboration.
- Customer Relationship Management: Organizations manage sales, customer interactions, and marketing campaigns using SaaS tools such as Salesforce.
- Project Management: Teams coordinate tasks and timelines through SaaS solutions like Asana or Trello.
- Human Resources: Companies handle payroll, recruitment, and employee management with SaaS HR platforms.
- File Sharing and Storage: Services like Dropbox and Google Drive allow users to store and share documents securely online.
- Accounting and Finance: Tools like QuickBooks Online help businesses manage their finances without installing local software.
Examples: Salesforce, Slack, Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, Zoom
Explore more of saas applications examples to get inspiration.
What is PaaS (Platform as a Service)?
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud-based solution that gives developers everything they need to build, test, and manage applications, all without the hassle of buying, configuring, or maintaining hardware and software infrastructure.
Instead of worrying about servers, storage, and networking, you can focus on coding and innovating, while the PaaS provider handles the rest.
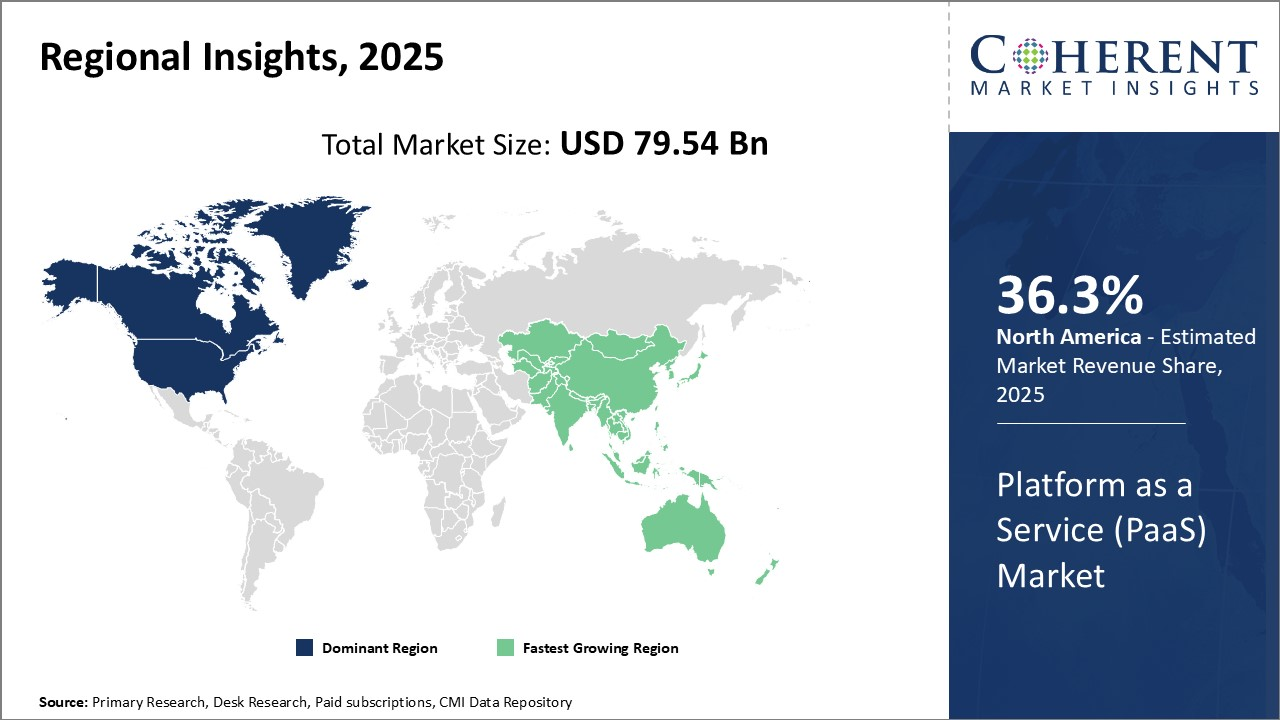
Source: Coherent Market Insights
The PaaS market is booming, by 2024, it’s valued at over $176 billion globally, fueled by businesses seeking faster, more cost-effective ways to build and launch applications.
As AI and generative development technologies become more mainstream, PaaS is evolving to offer specialized platforms for AI development, making it easier than ever to integrate advanced features into new apps.
Use Cases
PaaS is a favourite for businesses and developers who want to speed up software development and bring new products to market quickly. Some common scenarios include:
- Building web and mobile applications with built-in tools for development, testing, and deployment.
- Supporting Agile and DevOps teams with automated workflows and easy scaling.
- Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) or machine learning (ML) features into the app using ready-made APIs and platforms.
- Enabling distributed teams to collaborate on projects from anywhere, since everything is accessible via the cloud.
- Running analytics, business intelligence, or data management tasks without needing to manage complex backend systems.
Examples: Popular PaaS offerings include Microsoft Azure App Service, Google App Engine, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, IBM Cloud Foundry, and Heroku.
What is IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)?
IaaS, or Infrastructure as a Service, is like having a virtual toolbox for your business’s IT needs, delivered instantly over the internet. Instead of buying, installing, and maintaining physical servers and networking equipment, you rent computing power, storage, and networking from a cloud provider.
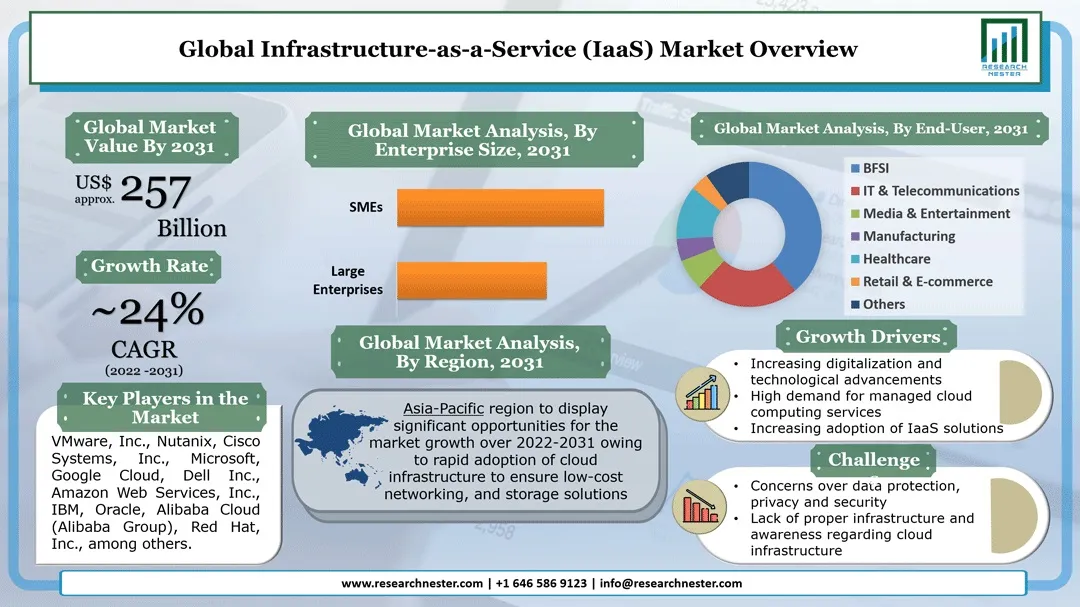
Source: Research Nester
You get the flexibility to scale up or down on demand and only pay for what you use, freeing you from the headaches and costs of managing hardware.
The IaaS market is on a rapid growth trajectory, expected to reach over $712.46 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate above 33%. What makes IaaS especially powerful is its ability to support everything from startups needing a single server to global enterprises running complex, distributed applications.
Use Cases
IaaS is the go-to solution for organizations that want to move fast and stay agile. Here’s how businesses are putting it to work:
Launching New Apps: Developers can spin up servers and storage in minutes, making it easy to test and deploy new software without waiting for hardware procurement.
- Disaster Recovery: IaaS offers a reliable backup plan – if your main systems go down, you can quickly restore operations from the cloud.
- Big Data Analytics: Need to crunch massive datasets? IaaS lets you tap into high-powered computing resources only when you need them.
- Website Hosting: From startups to global enterprises, companies host their websites on IaaS platforms for better performance and scalability.
- Temporary Workloads: Running short-term projects or seasonal campaigns? IaaS lets you scale resources up and down without long-term commitments.
Examples: AWS EC2, Google Compute Engine, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
Key Differences Between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS
Choosing the right cloud solution, whether SaaS, PaaS, or IaaS. It is a crucial step for any business looking to modernize its IT infrastructure or streamline operations. While you may already be familiar with what each model stands for, understanding their core differences will help you match your organization’s needs with the right level of control, flexibility, and ease of use.
Each model caters to different user profiles and business goals, so making an informed choice ensures you get the most value from your cloud investment.
| Aspect | IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) | PaaS (Platform as a Service) | SaaS (Software as a Service) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Audit your existing tools, software, and workflows. | A platform for developers to build and manage applications | Complete software solutions delivered online |
| Main users | IT admins, network architects | Developers, application creators | End-users, businesses needing ready-to-use apps |
| Management Responsibility | The user manages everything except hardware | Provider manages infrastructure; user manages apps/data | The provider manages everything |
| Customization | Highly customizable | Some customization (mainly in apps | Minimal customization |
| Technical Knowledge | High | Moderate | Not required |
| Focus | Infrastructure (VMs, storage, networks) | App Development tools and environments | End-user software |
| Example | AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure | Google App Engine, AWS Elastic Beanstalk | Google Workspace, Salesforce |
| Cost Model | Pay-as-you-go for resources | Pay-as-you-go for platform usage | Subscription or usage-based |
When deciding between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, think about your business’s technical expertise and the level of control you need.
- If you want to avoid managing infrastructure and simply use software, SaaS is the most user-friendly option. It’s ideal for businesses that want instant access to applications without worrying about updates or maintenance – everything is handled by the provider.
- PaaS, on the other hand, is perfect for developers who want to build and deploy applications quickly without dealing with the underlying hardware or operating system.
- IaaS gives you the most control and flexibility, making it suitable for organizations with in-house IT expertise that want to customize their infrastructure to specific needs.
In the end, your choice depends on your team’s skills, your needs for customization, and how much management responsibility you’re willing to take on. SaaS is best for simplicity and speed, PaaS is great for agile development, and IaaS is ideal for maximum control and scalability. Many organizations even combine these models to suit different workloads and business requirements.
Benefits of SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS
Now that you know about each type of cloud computing and the major differences between them. Now, let’s have a look at their benefits in a little more detail.
Benefits of SaaS (Software-as-a-Service)
- No Installation Hassles: Start using the software instantly – no downloads or setup required.
- Automatic Updates: Always get the latest features and security patches without lifting a finger.
- Anywhere Access: Use your apps from any device with an internet connection, perfect for remote work.
- Cost-effective: Pay only for what you use, with no need to buy expensive licenses or hardware.
- Worry-free Maintenance: The provider handles all the technical stuff, so you can focus on your business.
Benefits of PaaS (Platform -as- a -Service)
- Faster Development: Build and launch apps quickly thanks to ready-to-use development tools.
- No Server Management: Forget about setting up or maintaining servers – the platform does it for you.
- Easy Collaboration: Developers can work together smoothly, even from different locations.
- Scalable Solutions: Easily adjust resources as your app grows, without major headaches.
- Integrated Tools: Access built-in services for databases, analytics, and more, all in one place.
Benefits of IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service)
- Maximum Flexibility: Customize your infrastructure exactly how you want it, from storage to networks.
- On-demand Resources: Scale up or down instantly based on your current needs, no wasted capacity.
- Cost Savings: Only pay for what you use, avoiding big upfront investments in hardware.
- Full Control: You manage your operating systems, apps, and security settings.
- Disaster Recovery: Reliable backup and recovery options help protect your data and keep your business running.
Each model offers its own set of advantages, so the best choice depends on your goals, technical skills, and how much control you want over your cloud environment.
How to Choose the Right Model for Your Business?
Selecting the right cloud model for your business is all about matching your needs with the strengths of each service. As we’ve discussed the benefits and use cases, now it’s time to focus on your business’s unique requirements.
Consider the complexity of your operations, your team’s technical skills, your budget, and how much control you want over your IT environment. The right choice should support your current goals and be flexible enough to grow with your business, ensuring you get the most value and efficiency from your cloud investment.
Key factors to consider when choosing a cloud model:
- Technical expertise
- Budget
- Scalability needs
- Security requirements
- Customization level
- IT staff and resources
- Application and data portability
- Compliance specification
- Control and management level
Conclusion
At the beginning of 2019, more than 70% of companies and enterprises had shifted their operations to cloud computing. The main benefits they get are scalability, flexibility, and improved time to market.
Since each model has its plus and minus points, it’s important to know what is more valuable to you and your operations. And once you have made a decision, you need to find the right technology partner that goes with your business’s operations and helps you increase the productivity of your team.
Guru TechnoLabs carries out cloud application development projects relevant for companies of all sizes and across various domains. Contact us, benefit from cloud-based software, and manage all of your resources from a single location.
Frequently Asked Questions
SaaS delivers ready-to-use software over the internet, PaaS provides a platform for developers to build and deploy applications, and IaaS offers virtualized computing resources like servers and storage.
SaaS is the most user-friendly option for those with little to no technical knowledge, as the provider handles all maintenance and updates.
IaaS allows full customization of infrastructure, and PaaS offers some customization for app development, while SaaS typically offers limited customization options.
- SaaS: Google Workspace, Salesforce
- PaaS: Google App Engine, Heroku
- IaaS: AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure
SaaS usually follows a subscription model, PaaS and IaaS often use pay-as-you-go or usage-based pricing, allowing for flexibility based on your needs.
All three models offer scalability, but IaaS and PaaS provide more flexibility for scaling resources as your needs grow.
Yes, many organizations combine SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS to meet different needs, such as using SaaS for email, PaaS for app development, and IaaS for hosting custom infrastructure.














