How to Build a SaaS Application? A Detailed Guide on Types and Process

Software-as-a-service, or SaaS, has utterly dominated the software industry. Nowadays, 99% of companies use at least one SaaS application.
The process of creating a SaaS application is referred to as SaaS app development.
Although the recurring subscription model is well-established and widely used, there is much debate about how to truly create a high-quality SaaS product.
- Is it better to use low-fidelity or high-fidelity prototyping?
- How should agile development be applied?
- What is the best development framework for SaaS?
When you get into the details, nothing is clear-cut. To give you straightforward insights into the most crucial areas of development, we drew on our decade of experience building SaaS products.
What is SaaS Application?
A SaaS (Software as a Service) application is a type of software that runs on the cloud and can be accessed through the internet. Unlike traditional software that requires installation on a computer, SaaS applications are available on a subscription basis, making them an affordable and flexible choice for both businesses and individuals.
Users don’t have to worry about updates or maintenance because the service provider takes care of everything, including security and performance.
These applications are built using advanced web technologies to ensure smooth performance and security. Backend frameworks like Ruby on Rails, Django, and Node.js help manage the software’s functionality, while frontend technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript (including React, Angular, and Vue.js) create user-friendly interfaces.
However, To handle data, security, and scalability, SaaS applications rely on powerful cloud platforms like Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Salesforce Professional Services. These platforms ensure that the software runs reliably, stays up to date, and can grow with user demand.
Build Bespoke SaaS Solutions that Grow and Scale With You
Partner with us to build tailored SaaS solutions designed to adapt, grow, and scale
seamlessly with your business. Let’s innovate together!
Types of SaaS Applications
Software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications are extensively popular in the market and have become a new model of using cloud-based apps. By making their solutions easily available over the Internet, SaaS has greatly eliminated complicated installations and overhead costs and ensured scalability.
Today, there is a wide variety of SaaS app examples that affect industries, organizations, and companies by boosting their production, sharing of work, and processes. Here, you will find a breakdown of the various SaaS applications to understand how each fits into business needs.
1. SaaS Productivity Tools
Productivity applications are tools that enable teams to improve their output. These tools may include usual everyday products like communication apps or calendars through to noting and task management or project coordination applications. They enable the integration and coordination of tasks, increase productivity, and enable the organization of tasks in proper time.
Examples: Slack, Trello, Asana, Monday.com
2. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
CRM SaaS tools allow corporations to monitor and analyze customer operations and data at every phase of the purchase lifecycle. It makes customer service better, fosters sales, and helps customers stick with the businesses by streamlining the process of customer relations.
Examples: Salesforce, HubSpot CRM, Zoho CRM, Pipedrive
3. Marketing Automation Tools
Marketing automation SaaS solutions assist companies in creating, scheduling, executing, and tracking marketing tasks, such as email marketing, social media management, and lead generation. These tools allow organizations to reach the client base more accurately, monitor the outcome of promotions, and improve efforts accordingly.
Examples: MailChimp, Marketo, ActiveCampaign, HubSpot Marketing Hub
4. Accounting and Finance Tools
Accounting and finance SaaS apps help organizations handle their accounts receivable and payable, payments to employees, taxes, and generate reports. These solutions offer timely information and also help in the automation of financial processes that can make the management of a business easier.
Examples: QuickBooks, Xero, FreshBooks, Wave
5. Collaboration & Communication Tools
These tools primarily relate to streamlining internal communication between team members. Such tools are meant to help users to have smooth interactions including, chats, video calls, sharing, and exchanging of files or working on projects regardless of the distance between them.
Examples: Zoom, Microsoft Teams, Google Workspace, Dropbox
6. Human Resource Management Tools
HR SaaS applications are designed for managing employees, payroll, recruitment, performance appraisal, and other HR operations. These tools optimize HR activities, which in turn makes them easier to conduct and enables organizations to manage their employees.
Examples: BambooHR, Workday, Gusto, Lever
7. File Storage and Document Management System
Document management systems and file storage SaaS solutions are cloud-based services designed for safe storage, sharing, and administration of documents. They allow the files to be available from any device it is needed and secure data while facilitating collaboration in real time.
Examples: Google Drive, Dropbox, One Drive
8. Project Management Tools
SaaS tools for project management are intended to help in the planning, scheduling, and monitoring of projects. They enable the team to assign resources and schedule work, track results, and guarantee that all the goals of the project are achieved in the necessary time and cost.
Examples: Basecamp, Wrike, ClickUp, Teamwork
9. Customer Support and Helpdesk Software
These are SaaS applications, which aim to facilitate the delivery of excellent service to customers. They include live help or chat, ticketing systems, knowledge bases, and feedback mechanisms that help in quick and efficient handling of the customer’s problems.
Examples: Zendesk, Freshdesk, Intercom, Help Scout
By opting for the above-mentioned SaaS applications, businesses can streamline their operations, improve customer experiences, and upscale quickly.
Also Read: SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS: Which One to Choose?
How to Build a Saas Application? Step-by-Step Process
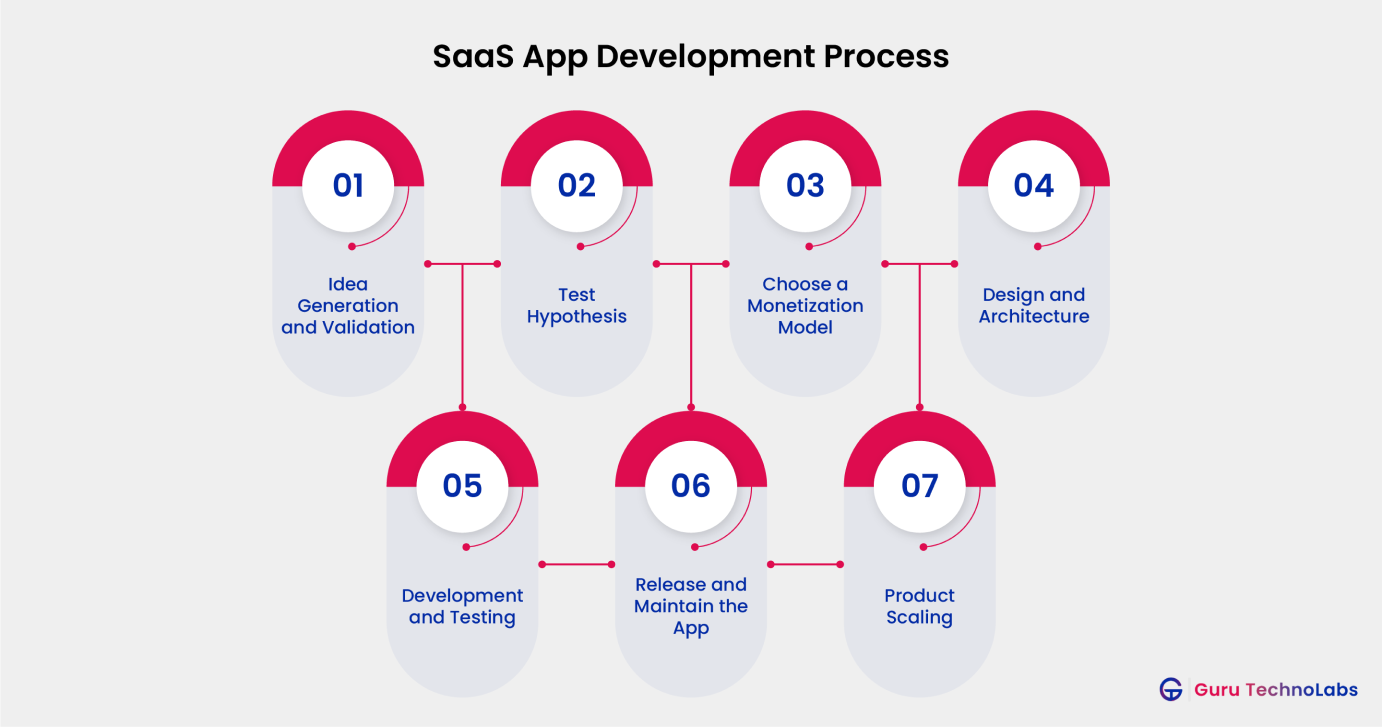
Developing a successful SaaS application is challenging and requires a combination of planning, design, and development to ensure the finest user experience. In the following section, we will examine the various steps and explore how each plays an important role in the entire process.
1. Idea Generation and Validation
The first process of SaaS app development is to develop a feasible idea to solve existing problems in the market. This idea is the basic functionality of your app and should, therefore, not be an assumption but a real need in the market.
- First, writing the idea should begin with choosing the target audience, their issues, and how your service or product will make their lives easier.
- Ideate and identify possible solutions based on an assessment of the current competition, customers’ wants and needs, and market shortcomings.
- This phase is critical since a good app idea can help to make the difference between success and failure.
Once you have a unique idea, you must validate it before starting the development process. You can do this through surveys, focus groups, or even by building a simple prototype and collecting user feedback. This validation stage will help you understand if your target audience is truly interested in your product and whether it’s something they would wish to pay for.
2. Test Hypothesis
It is crucial to test your hypothesis to verify that your SaaS product idea is viable. This involves testing different assumptions regarding the user’s requirements and needs, market appeal, and app viability.
The simplest way to enter the testing phase is to develop a first version, usually called a minimum viable product, that involves only the basic functionalities. Many startups choose the SaaS MVP development approach to quickly validate their ideas, minimize risk, and gather user feedback before scaling.
Several strategies for testing hypotheses include user interviews, A/B testing, or running pilot programs with a small segment of your target audience. You may also want to use analytics tools to track user behavior and identify friction or high-engagement areas.
3. Choose a Monetization Model
Choosing the right way to monetize is perhaps one of the most critical decisions when it comes to SaaS app development because monetization influences your revenue sources and the ability to sustain your business in the long run. One effective approach many businesses consider is offering white label software, allowing other companies to rebrand and resell the product as their own. The monetization model can target different types of audiences, and it is important to choose a model that would fit the target audience best.
There are some common SaaS monetization models such as:
- Subscription-based model: Users pay a periodic subscription fee as little as per month, quarter, or annum for using the app.
- Freemium model: There is a freemium version where some of the features they offer are available free of charge while others are available at a certain cost.
- Pay-as-you-go model: Consumers are charged based on the usage, for instance, the number of times the service is used or the amount of data used.
- Tiered pricing model: Has several pricing plans so that those who prefer consuming more or requiring more advanced features and functionalities may pay more.
- Enterprise model: Business, crafted to cover specific needs of large-scale companies through offering scalable pricing tiers and advanced capabilities.
Your monetization model should reflect the value you offer, your audience’s buying habits, along your long-term business strategy. Further, there must be an evaluation of the competition and customer base to determine which model enhances both the appeal to the customers and their retention.
4. Design and Architecture
When the core idea is confirmed, market fit, and a model for generating revenue, it is necessary to work on the design and architecture of the application. UX and UI must be followed while designing the application so that it is simple, fun, and comfortable to use.
Wireframing, prototyping, and the ability to make changes according to user input complete the design process. User interfaces should harmonize with your brand’s tone and tenderness to the target audience while being practical and sensitive to devices.
Technical, just like in any other software, the architecture of the SaaS app plays its part. These decisions relate to the choice of technology, how the app will grow in the future, and the security and robustness of the application server. Some decisions made during this phase include monolithic vs. microservices, which cloud infrastructure providers to use, and which databases and server configurations to use.
Scalability must be considered from the beginning since wrong decision-making frequently results in an application architecture incapable of handling users’ growing demands.
5. Development and Testing
The development stage is the one that involves bringing to life the idea and the sketches to develop a fully-featured SaaS app. It is therefore necessary to adhere to agile processes while developing, which involves slicing the development into sequences of smaller durations called sprints.
It allows for flexibility, constant feedback, and iteration while adapting and testing is a process. When developing an application, one needs to focus on the end-user view (front-end development) and the server-side view (back-end, database connectivity) at the same time.
With that, development should go hand in hand with thorough testing to identify issues and crashes that might hinder normal use of the app. Types of testing that should be incorporated include:
- Unit Testing: Makes certain that specific parts or elements of a program or software application work efficiently.
- Integration Testing: Makes sure that all components of the app function as expected when called upon from another component.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Ensures that the functions of the developed app meet the user requirements and demands.
- Security Testing: Protects the app from the probability of leakage of information, hacking, or unauthorized access.
The testing phase is crucial, if the application is not perfect; the users themselves will express their disappointment and dissatisfaction with the product, negatively influencing the brand’s image.
6. Release and Maintain the App
When your SaaS app is available for users, focus on evaluating your performance. In this step, you should focus on user feedback, evaluate it, identify what needs to be updated, and determine what new features you need to integrate. Simultaneously, SaaS developers on your team can assist you in updating and planning future modifications.
7. Product Scaling
Once you are done with the development and testing, launch the product and collect user feedback. This phase involves expanding the product to handle increased traffic, adding more features, and possibly targeting new markets. To scale quickly, you must ensure that your app’s infrastructure can handle the growth without compromising performance.
Challenges of SaaS App Development
It is not a cakewalk in the park to design an effective SaaS app, success does come at a cost. To plan, organize, control, and evaluate such challenges, it’s important to have a strategic plan from the start and, when needed, hire dedicated developers who have strong technical knowledge and the capabilities to overcome them.
Common Challenges in SaaS App Development:
- Ensuring users continue to find value in your app and stay subscribed after the initial sign-up.
- To build an architecture that can handle greater traffic and user data as well as not cause performance issues.
- Securing user data and preventing the app from any hack and other malicious activities or loopholes.
- Implementation of third-party applications, APIs, or legacy systems with the SaaS solution effectively.
- Storing good enough code or solutions as time passes, complicates future modifications and scaling.
- Sustaining the quick loading of pages with an increased number of users and keeping the interface highly interactive.
- Standing out in a crowded market with numerous SaaS solutions that may offer similar features.
- To mitigate these challenges, SaaS app development companies have to employ competent developers in various fields such as security, scalability, and usability.
For instance, Slack, a software company, had issues concerning scalability and reliability at some points of growth. This directly affected reliability and responsiveness which forced them to redesign the back-end and choose the right architecture for the application. Slack was able to address these growing pains well by hiring highly skilled developers, and also having a more scalable infrastructure.
How Much Does it Cost to Build Saas Application?
SaaS is a complicated cloud-based system that needs a large initial expenditure to get started and ongoing money to stay afloat. Depending on your market, resources, integration plan, and a host of other variables, the price of a SaaS MVP might range from $50,000 to $150,000.
Long-term expenditures like hosting, maintenance, and customer support must be taken into account in addition to the cost of developing a SaaS product. It’s also important to consider the costs associated with development, sales, and marketing.
Furthermore, when evaluating the cost of SAAS apps, one needs to consider more than just design and development expenses. Different nations have different wages, living expenses, and tax laws, which can have a significant impact on the final cost of developing an app.
Therefore, depending on the complexity of the project and the size of the development team, the cost of building a SAAS application development might vary greatly. It is advisable to speak with a development team or software development company to ensure an exact cost assessment of your project.
Want a clearer picture of your SaaS development expenses? Our detailed guide on software development costs that help you make informed budget decisions.
Final Words
Want to create a SaaS application because you have a fantastic idea? With the SaaS market expanding constantly, there is a vast amount of unrealized earning potential waiting for you.
However, you can encounter other obstacles, particularly time restrictions and a lack of talent. All you have to do is develop your app under the most recent industry trends, selecting the right app structure, monetization strategy, and essential features.
Guru TechnoLabs can support you at every step of the Software-as-a-Service development process and help you solve all of these problems. For a thorough consultation, get in touch with us, and let’s get your project started right away!