Top AI Agent Examples: Real-world Applications Across Industries

Not long ago, artificial intelligence (AI) seemed like something from the future, used only by big tech companies and research labs. Today, AI is a part of our everyday lives. It helps power things like Domino’s drone deliveries and Amazon’s personalized shopping suggestions. AI has grown from being a back-end tool to becoming the brain behind real-time decision making and customer engagement.
In fact, Gartner predicts that by 2028, over 33% of business software will include agentic AI. AI that can act on its own. This shows how fast AI is becoming a core part of how businesses operate.
One of the most exciting parts of this progress is the rise of AI agents. These are smart software programs that can do tasks on their own, often making decisions like a human would. In this blog, we’ll look at real-life examples of AI agents in different industries, how they work, what makes them useful, and why they’re becoming so important in today’s digital world.
What Are AI Agents?
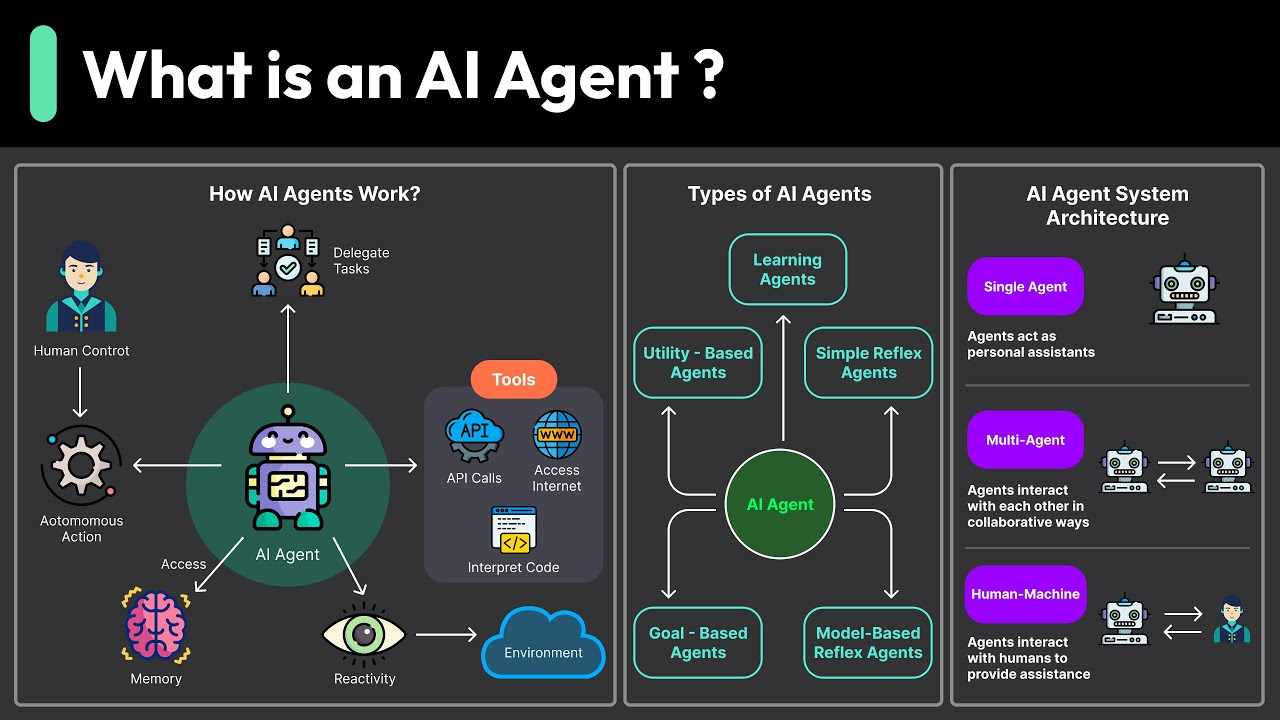
AI agents are smart computer programs that can think, make decisions, and complete tasks on their own, often without needing someone to guide them step by step. They can analyze data, learn from it, and take actions to reach specific goals.
- Some AI agents talk directly with people, like chatbots or virtual assistants, while others work behind the scenes to automate complicated tasks.
- For example, Google Assistant is a personal AI agent that helps with things like answering questions, setting alarms, and controlling smart devices at home.
- A more advanced example is Devin, an AI software engineer created by Cognition Labs. Devin can write, test, and fix code on its own, with little human help.
These examples show how AI agents are moving beyond simple tasks and starting to take on roles traditionally handled by people.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents come in many forms, each designed to solve different types of problems based on how much information they can process, how they make decisions, and how adaptable they are.
Below, we explore the major types of AI agents and their applications in real-world scenarios.
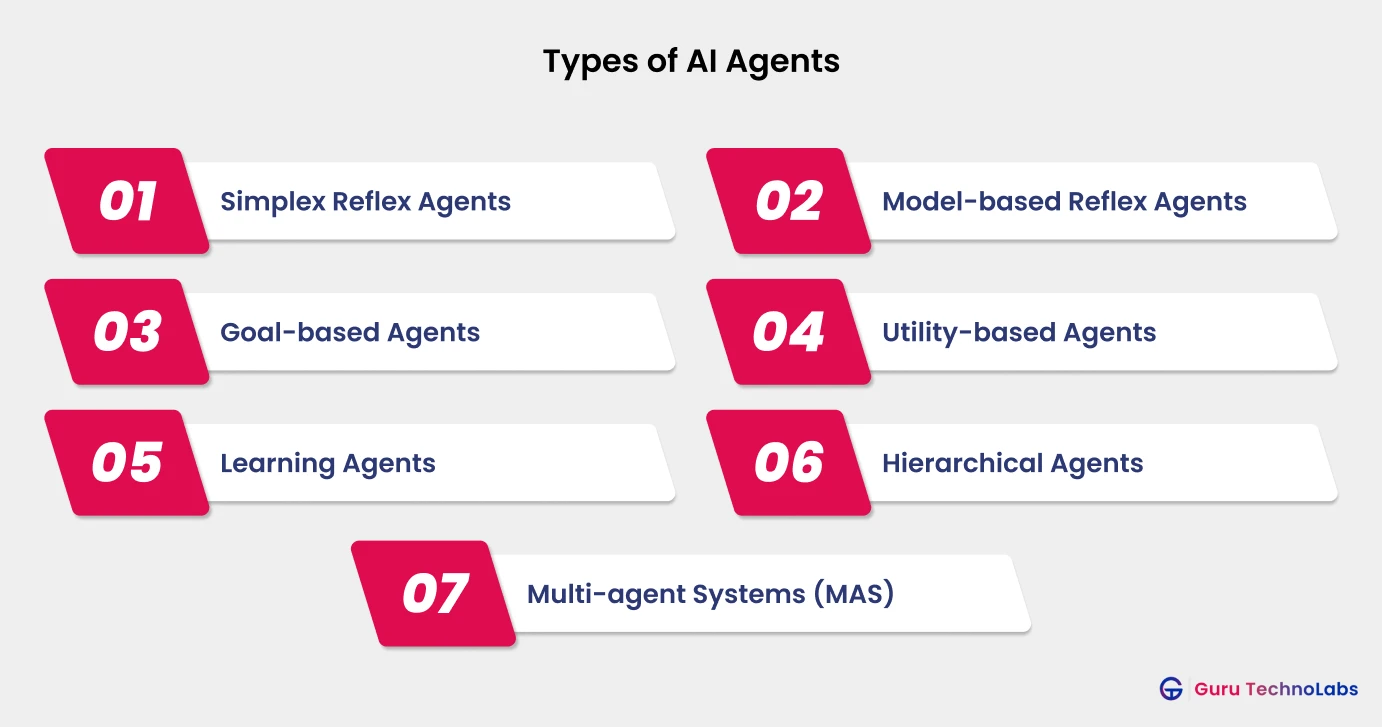
Simplex Reflex Agents
Simple reflex agents operate on a condition-action rule. They respond to the current percept without considering the past or future. These agents follow predefined rules to react to specific situations.
For instance, a thermostat that turns the heater on when the temperature drops below a certain level is a simple reflex agent. It doesn’t remember past temperature; it just acts based on current input.
Model-based Reflex Agents
These agents go a step further by maintaining some internal state or model of the world. This model helps them make more informed decisions by considering previous perceptions and current conditions.
For instance, a robot vacuum cleaner that remembers the layout of a room and avoids areas it has already cleaned is model-based. It doesn’t clean randomly, it uses a model of the environment to decide where to go next.
Goal-based Agents
Goal-based agents make decisions by considering their goals and choosing actions that help them achieve those goals. Unlike reflex agents, they evaluate potential outcomes before acting.
For example, navigation apps like Google Maps use goal-based logic to find the best route to a destination. Similarly, travel companies use AI to recommend flight and hotel combinations that align with a user’s trip preferences and budget, ultimately helping them achieve their travel goals.
Utility-based Agents
These agents aim not just to achieve a goal, but to do so in the best possible way. They assign a utility value to each outcome and choose the action that maximizes overall satisfaction or benefit.
An AI in a smart home that decides whether to open windows, turn on fans, or use air conditioning based on comfort levels and energy savings is utility-based. It chooses what brings the most benefit with the least cost.
Learning Agents
Learning agents improve over time by learning from their experiences. They adapt their behaviour based on feedback from the environment or user, becoming more effective with continued use.
An example is a spam email filter that continuously improves its accuracy based on user feedback.
Hierarchical Agents
Hierarchical agents break down complex tasks into manageable sub-tasks, organizing decision-making into layers or levels. This structure helps manage complexity and improves efficiency in decision-making.
In robotics, a hierarchical agent might have high-level goals like “clean the room”, which are broken into sub-goals such as “go to the living room”, “detect dirt”, and “start vacuuming”.
Multi-agent Systems (MAS)
A multi-agent system involves multiple agents interacting with each other, either cooperatively or competitively, to solve problems that are too complex for a single agent. These agents may share information, coordinate actions, or negotiate to reach shared goals.
For instance, online multiplayer games where different characters interact or cooperate.
Why Are AI Agents Gaining Popularity?
AI agents are rapidly transforming how businesses and individuals interact with technology. Their rise in popularity isn’t just a trend, it reflects a shift toward intelligent systems that can think, adapt, and act independently.
Unlike traditional software, AI agents can operate continuously, learn from their environment, and make real-time decisions without human intervention. This makes them invaluable across industries, from customer service and finance to manufacturing and smart home ecosystems.
What’s driving this momentum is not just automation but generative AI development, which allows AI agents to generate content, simulate decision-making scenarios, and handle creative or unpredictable tasks with increasing sophistication.
Key reasons for their surge in popularity:
- Autonomy with intelligence
- Real-time adaptability
- Scalable decision making
- Integration with generative AI
- 24/7 productivity
- Data-driven actions
As businesses push for smarter automation and personalized user experiences, AI agents are no longer optional, they’re becoming essential.
Top AI Agent Examples by Category
If you look around, you’ll see many AI agents already at work and in daily lives, across the domains and sectors. Here are real-world examples to show their capabilities.
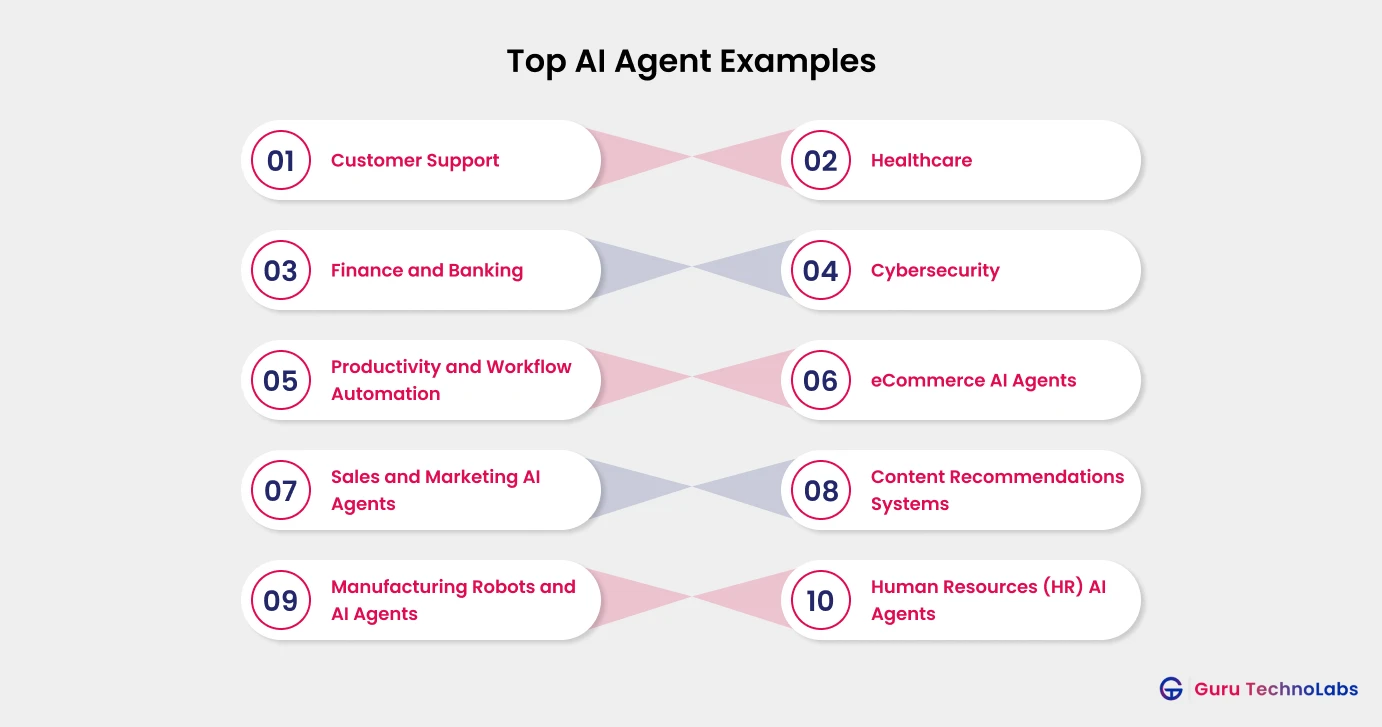
Customer Support AI Agents
- ChatGPT (OpenAI): Used by businesses to answer customer questions in real-time, generating human-like responses and reducing the need for human agents for repetitive queries.
- Ada Support: Automates responses to frequently asked questions on eCommerce websites, speeding up customer service and improving accuracy.
- IBM Watson Assistant: Helps companies build chatbots that can handle complex customer queries and connect with backend systems for smooth support.
- Zendesk AI Bot: Routes support tickets, prioritizes issues, and resolves common problems automatically, making customer service faster and more efficient.
Healthcare AI Agents
- Babylon Health: Offers AI-powered health diagnostics, combining symptom checkers with virtual doctor consultations to help users understand their health and access care quickly.
- PathAI: Assist doctors by analyzing medical images for signs of diseases like cancer, improving the accuracy of diagnostics.
- Olive: Automates hospital administrative tasks such as patient registration, insurance claims, and billing, freeing up staff for more critical work.
- Corti: Listens to emergency calls and helps identify critical symptoms in real time, supporting emergency responders in making quick, accurate decisions.
Finance and Banking AI Agents
- J.P. Morgan (Kasisto’s AI): Uses conversational AI agents to help clients manage accounts, answer financial questions, and detect suspicious activities, providing 24/7 intelligent banking support.
Cybersecurity AI Agents
- Darktrace: Deploys AI agents that monitor company networks, detect cyber threats, and autonomously respond by isolating compromised devices or accounts, acting as digital security guards.
Productivity and Workflow Automation AI Agents
- Zowie: Automates customer support for online stores, handling returns, exchanges, refunds, and order tracking across chat, email, and social media. It’s used by brands like Monos and Booksy to cut costs and scale globally.
- Hypotenuse AI: Creates product descriptions and SEO content in bulk, helping eCommerce businesses quickly launch new products and keep listings fresh.
- Gorgias + ChatGPT: Resolves customer inquiries, manages tickets and provides personalized recommendations, improving both support and sales conversion.
- Yuma AI Chat: Delivers instant, accurate answers to customer questions on online stores, streamlining the shopping experience.
eCommerce AI Agents
- Otio: AI research and writing partner for students and professionals, helping with brainstorming, planning, writing, and editing of documents or research papers.
- Lindy: Automates email management by sorting, replying, and following up on emails, and syncs updates with tools like CRM or Slack, saving hours of manual work.
- Agent Swarms (Lindy): Allows multiple AI agents to run parallel tasks, such as preparing for customer calls or scraping data, multiplying team productivity without extra hires.
Sales and Marketing AI Agents
- Jasper AI: Generates long-form marketing content like blog posts, landing pages, and guides, enabling marketing teams to scale content creation.
- Copy.ai: Specializes in short-form campaigns such as emails and ad copy, making it easier to run targeted marketing efforts.
- Writesonic: Produces ads, product descriptions, and social media captions, helping brands maintain a consistent and engaging online presence.
Content Recommendations Systems
- Amazon’s Recommendation Engine: Suggests products based on browsing and purchase history, increasing sales and customer satisfaction.
- Netflix’s Recommendation System: Recommends movies and shows tailored to each user’s preferences, keeping viewers engaged (general industry knowledge).
- Spotify’s Discover Weekly: Uses AI to curate personalized playlists for users, enhancing music discovery (general industry knowledge).
Manufacturing Robots and AI Agents
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Work alongside humans on factory floors, handling repetitive or dangerous tasks to boost safety and efficiency.
- Predictive Maintenance Agents: Monitor equipment health and predict failures before they happen, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Quality Control AI: Inspects products for defects using computer vision, ensuring high-quality output without manual inspection.
Human Resources (HR) AI Agents
- Acme’s AskHR (IBM): Automates HR workflows, handling onboarding, payroll, and internal assessments. It manages millions of employees’ interactions annually, saving thousands of hours and significant costs.
- DianaHR: An AI-driven HR assistant for small and mid-sized companies, managing compliance, benefits, onboarding, and employee inquiries.
- GoodTime (HelloFresh): Schedules interviews and coordinates hiring, reducing time-to-hire and administrative workload.
- Unilever’s AI Hiring System: Screens candidates using AI-analyzed video interviews and game-based assessments, providing personalized feedback and improving hiring efficiency.
- LeapIn (Hilton): Uses AI to match candidates to roles based on skills and company values, reducing turnover and speeding up hiring.
- Levity: Automates onboarding workflows, ensuring forms are completed, policies shared, and training scheduled.
- Introist: Handles automated employee offboarding, sending surveys, managing asset returns, and scheduling exit interviews.
- General HR AI Agents: Automate candidate sourcing, resume screening, onboarding, answering HR policy questions, and employee engagement analysis.
Well, the list can be long, but the above AI agents are already making a big impact across sectors by handling repetitive tasks, supporting critical decisions, and freeing up humans to focus on more creative or strategic work. Their ability to learn and adapt means their influence will only grow in the years ahead.
Choosing the Right AI Agent for Your Business
Choosing the right AI agent is a strategic decision that can drive efficiency, innovation, and growth. Here are steps to help you make the best choice for your organization:
- Define your business needs and use cases
- Understand the type of AI agents
- Evaluate integration and compatibility
- Prioritize security, privacy, and compliance
- Assess customization and industry fit
- Consider ease of use and support
- Plan for scalability and future growth
- Test, measure, and iterate
Let’s have a quick look at the table and check considerations to make while choosing the right AI agent for your business.
| Step | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Define business needs | What problems are you solving? How complex are your workflows? |
| Know agent types | Automation, conversational, or multi-agent? |
| Integration | Can it connect with your current systems? |
| Security & Compliance | Does it protect sensitive data and meet regulations? |
| Customization & Industry fit | Is it tailored for your sector, and can it use your data? |
| Ease of use & support | Is it user-friendly and well-supported? |
| Scalability | Will it grow with your business? |
| Test & measure | Can you pilot, monitor, and improve the solution? |
The best AI agent for your business is one that aligns with your goals, integrates with your systems, and is secure, scalable, and easy to use. Start with a clear understanding of your needs, evaluate solutions carefully, and choose an experienced AI development company that can adapt as your business evolves.
Conclusion
AI Agents are no longer confined to sci-fi movies; they’re actively changing how businesses operate and how we interact with technology. From healthcare to manufacturing to eCommerce to retail, AI agents are proving their worth across various domains.
Whether you are a business leader, a startup owner, or a well-established entrepreneur, understanding AI agents is important these days. They represent not just a technological advancement but a significant shift in how we run businesses and make decisions in this digital age.
Ready to enter the future with Guru TechnoLabs’ AI Agents? Schedule a call now!
Frequently Asked Questions
An AI agent is an AI-powered software entity that makes decisions and takes actions without human intervention, using real-time information from internal and external sources.
An AI agent perceives its environment and takes actions towards a specific goal. For instance, an autonomous AI in self-driving cars that processes sensor data to direct or AI trading bots that analyze markets and execute trades.
Yes. GPT is a large language model and acts as an interactive AI assistant. It inputs and generates responses but does not independently act in an environment like autonomous AI agents.
They handle repeat tasks, while humans focus on more productive tasks and high-empathy work.
Yes. Siri qualifies as an AI agent because it is built to autonomously carry out tasks like setting reminders, responding to user queries, and following voice instructions after receiving a prompt. Siri’s ability to interpret requests and act on them without further human intervention is a hallmark of AI agent functionality.










